 By Eliza Popova
By Eliza Popova
According to the company, Hala Point processes information 50 times faster and uses 100 times less energy than traditional computing systems. Intel states that scientists will be able to use a machine to conduct artificial intelligence research. Traditional computers process information linearly. They rely on central processors (CPU) and graphic processors (GP). And neuromorphic computers use artificial neurons and synapses similar to the biological brain.
These networks help neuromorphic computers simultaneously process a lot of information and make calculations in parallel. Such a machine can handle up to 20 quadrillions of operations per second (20 Petaos), while maintaining excellent energy efficiency - more than 15 trillions of operations per second per OJSC. Simply put, Hala Point can even bypass some of the fastest supercomputers in the world.
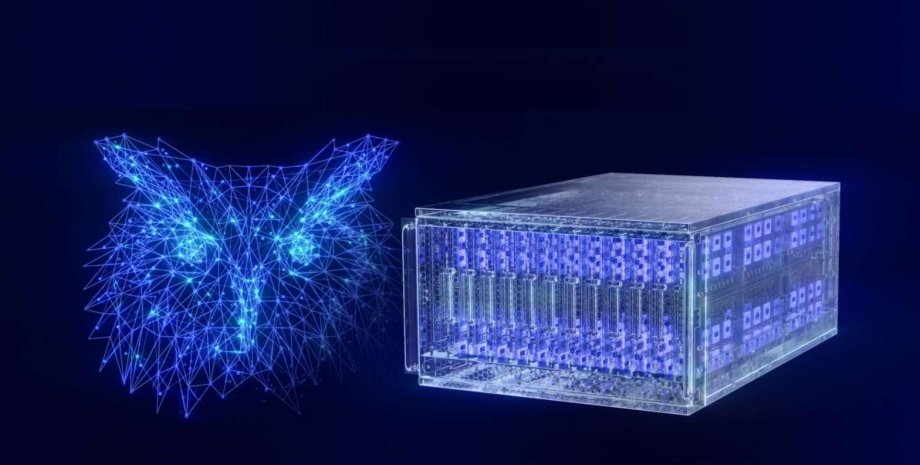
When performing the SI-TV, the device consumes 2600 watts of energy, which can be compared to the power of the household appliance. The HALA Point computer operates on the Neuromorphic Intel Loihi 2 Hala Point processor, consisting of 1152 LOIHI 2. The processor supports up to 1. 15 billion artificial neurons and 128 billion synapses. In other words, the power of the neurons of this system is equivalent to the power of the owl or small monkey.
Researchers at the National Laboratory of Sandy plan to use Hala Point for complex scientific computing tasks in areas such as devices physics, computer architecture, computer science, scientific modeling. But so far the machine is at an early stage of development and is not a consumer product. However, scientists are confident, it will affect the next generation of neuromorphic computing systems.
It can be used in several applications that require real -time decisions, for example, to manage a "smart" city. In addition, the device opens the path to a more sustainable future, as it reduces the enormous energy needs associated with neuromatic training. Intel intends to transform a neuromorphic computer from a research prototype into a leading sectoral commercial product in the coming years. Earlier, we reported that a smart "box" Brainchip works on brain -like chips.
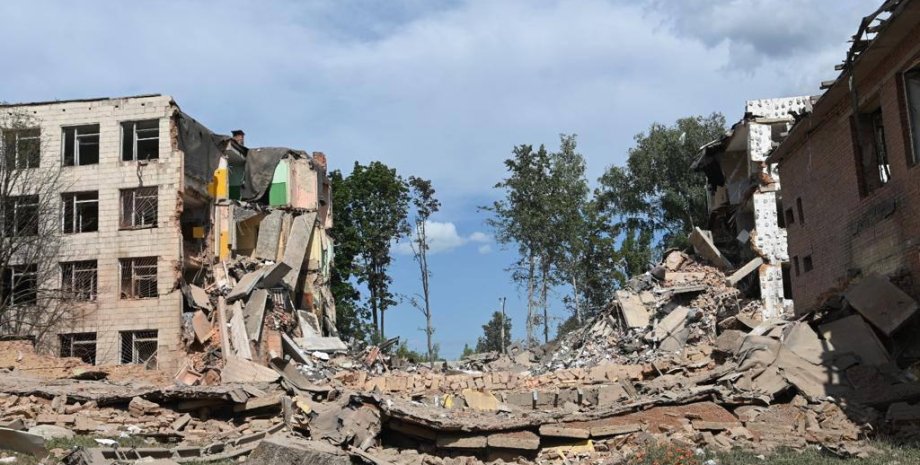
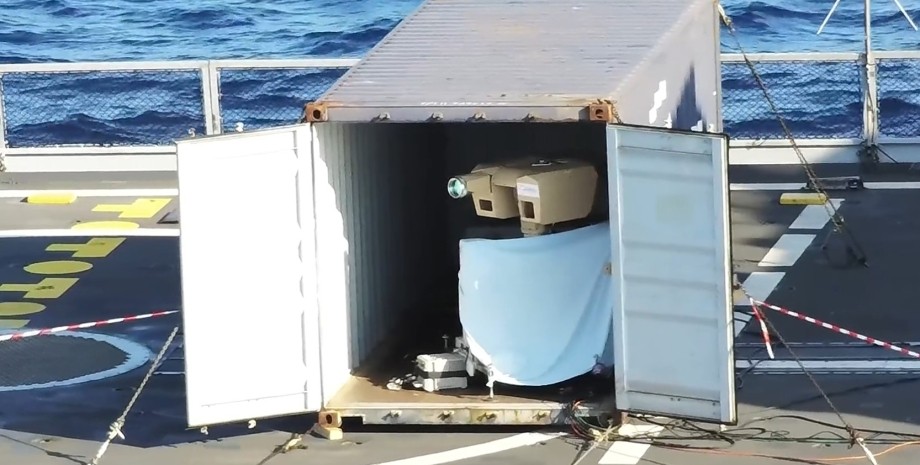
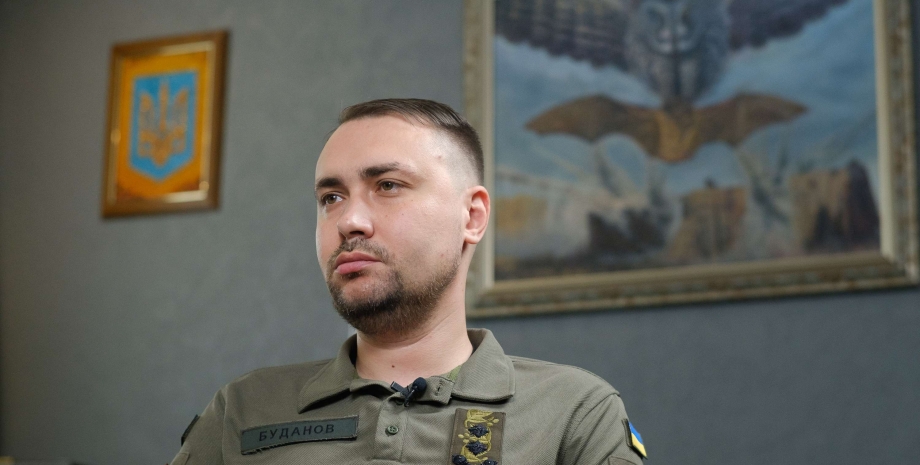
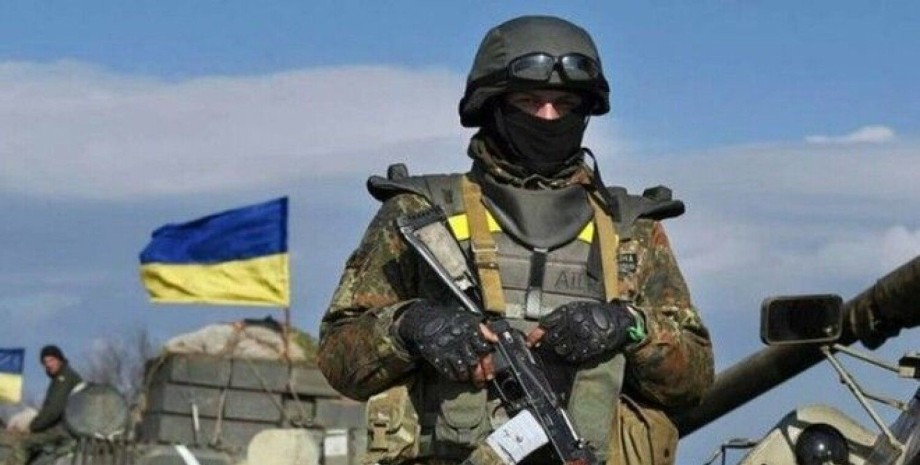










All rights reserved IN-Ukraine.info - 2022